
Blood test (RAST)
A small amount of blood is taken to look for the antibodies created to fight the cow’s milk protein – these are called Immunoglobulin E (IgE).
The pathway to a clear diagnosis is a step-by-step process. We’ll help you understand those steps, so you feel prepared for the journey and any visits with your Healthcare Professional.

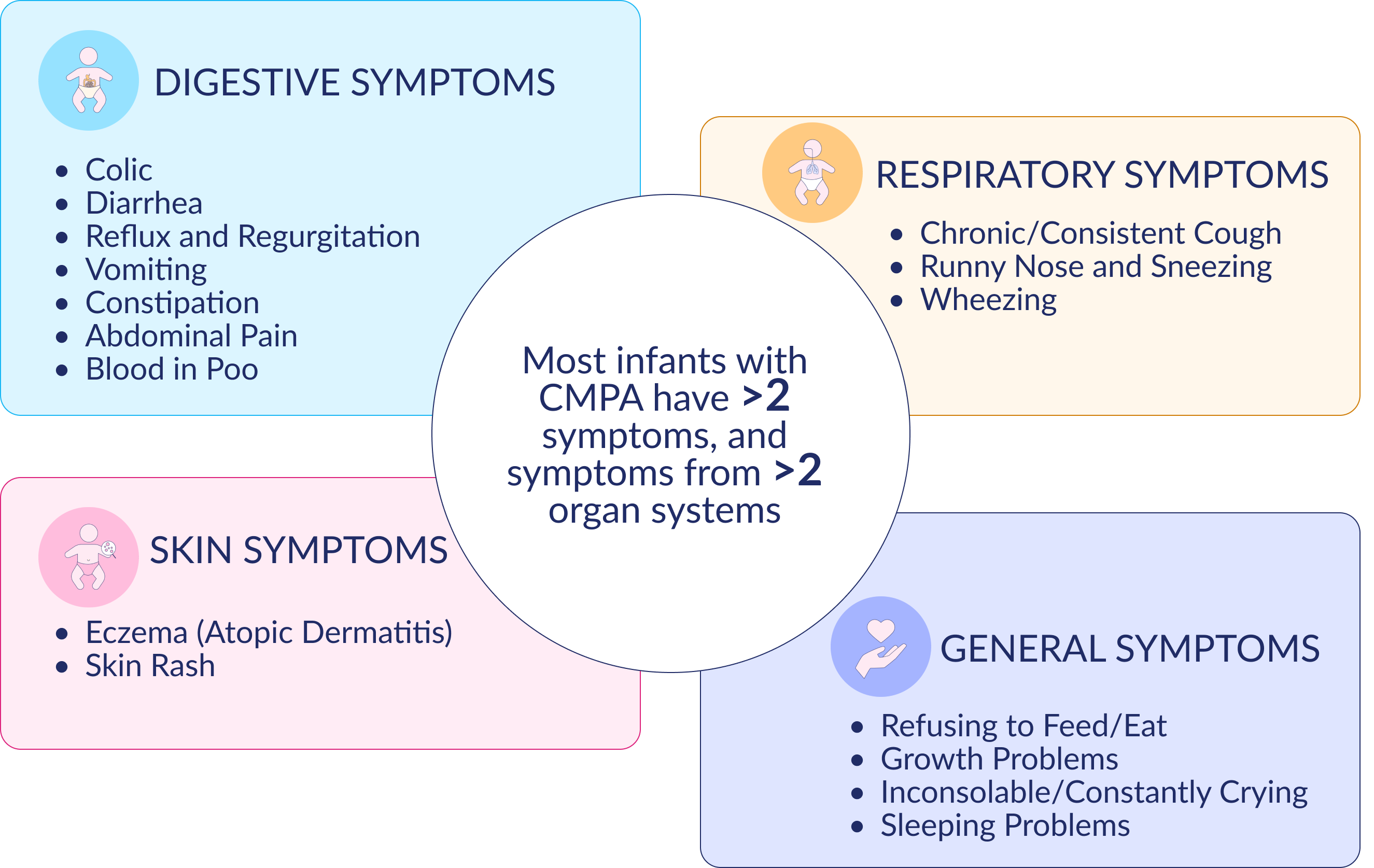
DIGESTIVE
Up to 60% of infants with CMPA have digestive symptoms
RESPIRATORY
Up to 30% of infants with CMPA have respiratory symptoms
ANAPHYLAXIS
Anaphylactic shock is a severe, immediate, allergic reaction, which can affect many parts of the body
SKIN
Up to 70% of infants with CMPA can have skin-related symptoms
GENERAL SYMPTOMS

Babies with CMPA usually experience more than just one symptom and these symptoms can be very different from one baby to the next. Therefore it is always best to discuss it with your baby’s Healthcare Professional. They will look at the symptoms in detail and often use a symptom scoring system to decide if it is related to CMPA.
Your Healthcare Professional will examine your baby and ask you some questions around your baby's diet and their symptoms. If cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA), is suspected, your Healthcare Professional may then perform specific allergy tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include a blood test, skin prick test or elimination diet followed by food challenge.

A small amount of blood is taken to look for the antibodies created to fight the cow’s milk protein – these are called Immunoglobulin E (IgE).
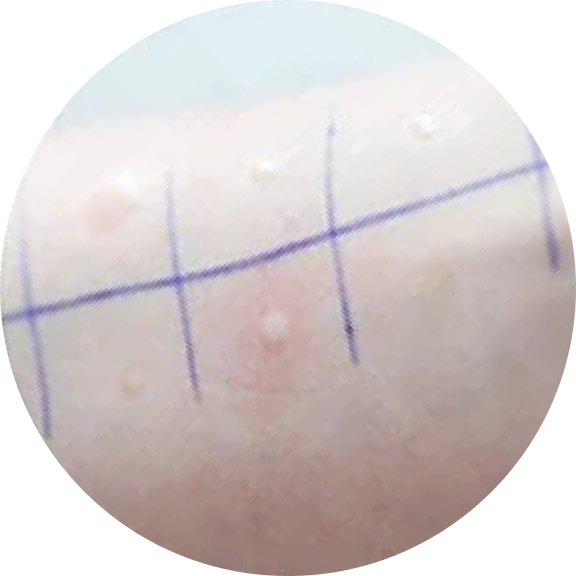
The skin is scratched first and a tiny amount of the food/allergen is added to the skin.
It is important that you do not experiment with a cow’s milk-free diet for your baby without recommendation and guidance from your Healthcare Professional. Based on the age of your baby and the severity of the symptoms, your Healthcare Professional will recommend the most suitable solution.
The best way for your Healthcare Professional to confirm or exclude the diagnosis of CMPA is through an elimination diet, which involves eliminating cow’s milk proteins from your baby’s diet, followed by food challenge, in which cow’s milk protein is reintroduced in a controlled office setting with a healthcare professional present.
If the diagnosis of CMPA is confirmed, the good news is that with the support of your Healthcare Professional, CMPA can be managed.
Diagnosis of CMPA should not impact on your breastfeeding routine. Mothers are encouraged to continue breastfeeding even when their babies have CMPA. This usually requires qualified dietary counseling to completely exclude all sources of cow’s milk protein from the mother’s diet. Vitamin D and calcium supplements might be recommended by your Healthcare Professional.

CMPA can be managed easily with the right dietary changes and feeding. When breastfeeding is not an option, your Healthcare Professional will decide on which tailor-made solution best suits your baby's needs.
Learn more

There are solutions for every family. Hear from other families affected by CMPA and get tips on everything about feeding your baby.
Learn more